Configuration files for Apache are located within the /etc/httpd/conf.d/ directory. Any file with the.conf extension is processed in alphabetical order in addition to the module configuration files in /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/, which contains any configuration files necessary to load modules. The Apache HTTP daemon supports name-based hosting so that multiple domain names can share one IP address. Changing a host name effectively changes your website's domain name, since your visitors request the site by sending its host name, in the form of a URL, to your specified port in the request's HTTP headers.
The Apache HTTP Server, httpd, is an open source web server developed by the Apache Software Foundation. If you are upgrading from a previous release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, you will need to update the httpd service configuration accordingly. This article tells you how to download, install and configure Apache webserver on your Windows based computer to host a webpage. Go to www.apache.org and download the latest version of Apache's webserver.
Free Domain Hosting (for already registered domains) NEW - Starting with, ALL domain extensions are accepted, including the new, long TLDs. If you don't have your own domain, register one here then create your free hosting account using the form below.
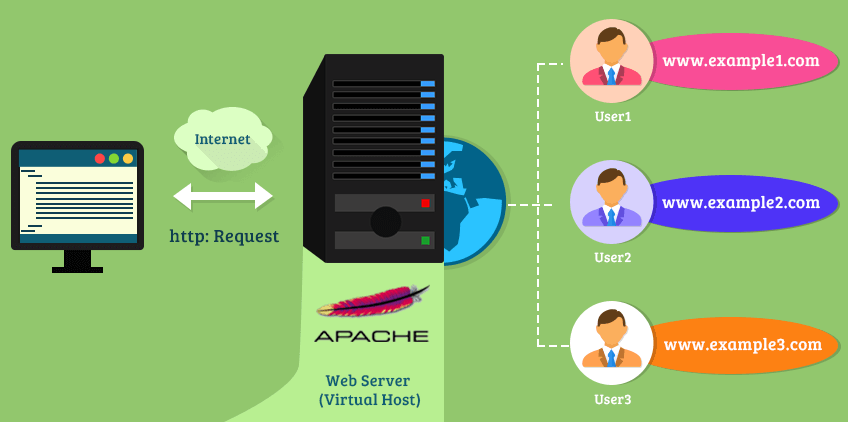
Using Apache Virtual Host, you can run several websites on the same server.
For example, I can run both thegeekstuff.com and top5freeware.com on a single physical server that has one Apache webserver running on it.
Fig: Apache Virtual Host (Multiple websites, one Apache)
There are two types of Apache virtual host configurations: 1) IP-Based Virtual Host and 2) Name-based Virtual Host. Name-based virtual host is recommended for most scenarios.
IP-Based Virtual Host

In this configuration, when you are pointing two websites (with different ip-address) to the server that runs Apache, that physical server should have two different ip-address configured.
This means that the server should have two ethernet cards, each one of them configured to the ip-address of the corresponding website that Apache virtual host will be serving. So, this is not practical for most aspects, and you should not be using this.
In the following example, the server contains two NIC cards, one is configured with 192.168.101.1 ip-address for thegeekstuff.com, another is configured with 192.168.102.1 for top5freeware.com. Both these ip-address are served by a single Apache webserver running on that server using IP-Based virtual host.
Name-Based Virtual Host
In this configuration, when Apache webserver receives a request, it looks for the hostname in the HTTP header, and depending on the hostname, it servers different websites. This is very easy, as you need only one ip-address on that physical server; but, you update the DNS with multiple website names pointing to the same ip-address. For all practical purpose, you’ll be using only Name-based virtual host configuration.
In the following example, the server contains only one NIC card, which is configured with 192.168.101.1 ip-address. The DNS entry for both thegeekstuff.com and top5freeware.com website points to 192.168.101.1 ip-address. When Apache recives a request, it looks for the hostname entry in the HTTP header, and serves the corresponding website.
Fig: Apache Name-Based Virtual Host
Apache Http Post Json
1. Uncomment httpd-vhosts.conf in httpd.conf
If you’ve installed Apache 2 from source, by default, the following line will be commented in the httpd.conf file. Uncomment this line.
2. Setup virtual hosts
Modify the httpd-vhosts.conf as shown below to setup named-based virtual host setting for two hosts. Best macbook for video editing.
- NameVirtualHost *:80 – Indicates that all the name-based virtual hosts will be listening on the default port 80
- <VirtualHost *:80> </VirtualHost> – Enclose all the apache configuration parameters for each and every virtual host between these VirtualHost tags. Any apache directives can be used within the virtualhost container.
- In the following example, we are setting up virtual host for thegeekstuff.com and top5freeware.com listening on the same port 80. So, there will be two <VirtualHost *:80> </VirtualHost>, one for each website.
- When you go to thegeekstuff.com, the files under /usr/local/apache2/docs/thegeekstuff will be served by Apache; and the access_log and error_log for this site will go under /usr/local/apache2/logs/thegeekstuff
3. Check VirtualHost Configuration Syntax
Verify virtual configuration syntax using “httpd -S” as shown below. When everything is setup properly, it just displays “Syntax OK”.
When something is not configured properly, it will display warning message, including “directory does not exit” message as shown below.
4. Restart the Apache and test
Now, when you go to thegeekstuff.com (or www.thegeekstuff.com), the apache will serve the files from /usr/local/apache2/docs/thegeekstuff directory.
Apache Http_host Variable
Apache Web Server Windows
When you go to top5freeware.com (or www.top5freeware.com), the same apache running on the same server will serve the files from /usr/local/apache2/docs/top5freeware directory.
Just to reiterate, for the name-based virtual host to work properly, the DNS entry for both these websites should be pointing to the same external ip-address of the physical server where the Apache webserver is running.
